Equality
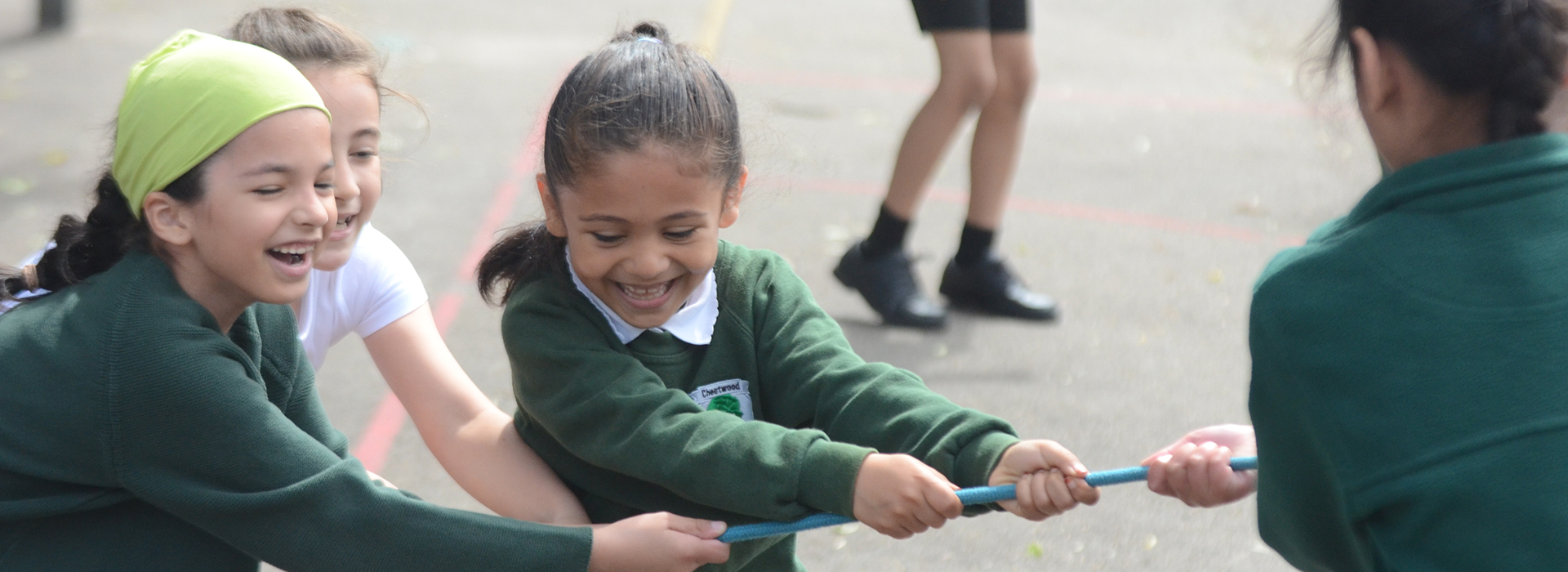

The Equality Duty (2012) provides a single, consolidated source of discrimination law, covering all the types of discrimination that are unlawful. The term ‘protected characteristics’ is used as a convenient way to refer to the categories to which the law applies.
The eight protected characteristics are:
- Race
- Disability
- Sex
- Gender Reassignment
- Pregnancy and maternity
- Age (as an employer)
- Religion or belief
- Sexual orientation
The Public Sector Equality Duty 2011 has three aims under the general duty for school and academy settings:
- To eliminate unlawful discrimination, harassment and victimisation and other conduct prohibited by the Act, by removing or minimising disadvantages suffered by people due to their protected characteristics.
- To advance equality of opportunity between people who share a protected characteristic and those who do not, by taking steps to meet the needs of people from protected groups where these are different from the needs of other people.
- To foster good relations between people who share a protected characteristic and those who do not, by encouraging people from protected groups to participate in public life or in other activities where their participation is disproportionately low.